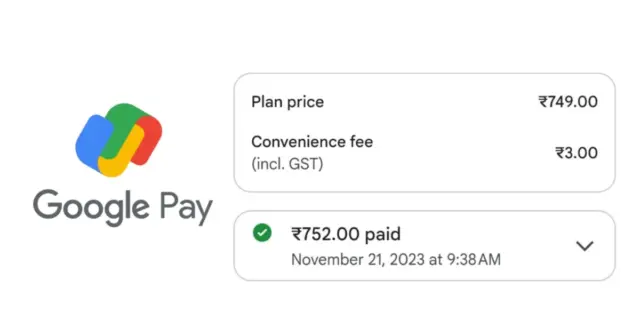
Google Pay has introduced convenience fees for bill payments made using credit and debit cards. This change impacts users who pay utility bills, phone bills, and other bills through the platform. The move alters Google Pay’s previously free service for card-based bill payments.
The new charges vary depending on the bill amount and the card type. Users see the fee before confirming their payment. Google Pay displays the exact amount charged. This allows users to decide whether to proceed with the transaction. The fee structure is not a fixed percentage. It is calculated based on various factors. These factors include the biller, the payment amount, and the card network.
This decision by Google Pay comes as digital payment platforms face increasing operational costs. Maintaining the infrastructure, processing transactions, and ensuring security require significant investment. Other payment platforms have also started implementing similar charges. These charges help offset these costs. The fees allow Google Pay to continue offering its services.
Google Pay users still have free payment options. Payments made through Unified Payments Interface (UPI) remain free. UPI allows direct bank-to-bank transfers. This method bypasses card networks. It is a popular choice for smaller transactions. Users can link their bank accounts to Google Pay for UPI payments.
The introduction of fees for card-based bill payments could influence user behavior. Some users may switch to UPI for bill payments. Others might choose alternative payment methods. The impact of this change on Google Pay’s user base remains to be seen. Competition in the digital payments sector is intense. Users have several options available.
Google Pay has not released an official statement explaining the reasons behind the new fee structure. Information about the fees is available within the app during the payment process. Users can view the fee before completing their transaction. This transparency allows users to make informed decisions.
The move by Google Pay reflects a broader trend in the digital payments industry. As the industry matures, platforms are exploring ways to monetize their services. Convenience fees for card-based transactions are one approach. This approach helps platforms cover operational costs and ensure long-term sustainability.
The new fee structure applies to various bill categories. These categories include electricity bills, water bills, mobile recharges, and DTH recharges. The fees are consistent across different billers. However, the exact amount can vary based on the factors mentioned earlier.
Users who frequently use Google Pay for bill payments will be most affected by this change. They will now incur additional charges for card-based transactions. Those who primarily use UPI will not be impacted. The change highlights the importance of understanding the different payment methods available. It also encourages users to explore cost-effective options.
The long-term effects of this change are uncertain. It is possible that other digital payment platforms may follow suit. The introduction of fees could become a standard practice in the industry. This could reshape the landscape of digital payments. Users may need to adapt to new fee structures across different platforms.
The introduction of fees might lead some users to reconsider their payment habits. They might explore traditional payment methods or switch to platforms that offer free card-based transactions. The digital payments industry is dynamic. User preferences and market conditions can change rapidly.
Google Pay’s decision to implement convenience fees for card-based bill payments is a significant development. It marks a shift in the platform’s pricing strategy. The impact of this change will be closely watched by users and competitors alike. The move highlights the ongoing evolution of the digital payments industry.


















